As part of the Visual Timeline series, this pages highlights key events in China.
Oversimplified Chinese dynasties timeline:

Another with a little more detail on the ‘smaller’ dynasties:

Until the Qin dynasty unified in 221BC, China was a disparate land of hundreds of polities.
~2000BC: Xia dynasty (2205BC-1766BC). Three Dynasties period. 3,000 polities.
~1500BC: Shang dynasty (1600BC-1046BC) – bronze and writing. 1,800 polities.
1046BC: Western Zhou dynasty (1046BC-250BC) – iron and philosophy. 170 polities.
770BC: Eastern Zhou dynasty, Spring and Autumn period (770BC-476BC). 23 polities.
600BC: Grand Canal construction begins to link China’s two busiest rivers, Yellow River and Yangtze.

563BC: Buddha born
551BC: Confucius born (551BC-479BC)

475BC: Eastern Zhou dynasty, Warring States period (475BC-221BC). 7 polities.
262BC: Battle of Changping, part of Qin unification wars, 700k casualties, deadliest known conflict up to this date.
221BC: Qin dynasty unifies China into 1 polity.
210BC: First Qin emperor Qin Shi Huang buried with Terracotta Army for afterlife.

206BC: Han dynasty begins (206BC-220AD), overthrows Qin.
140BC: Emperor Wu (r. 140BC-87BC) expands Han empire
By turn of millennium, Roman empire and Han dynasty are comparable in size, population (50m-100m), and power.

With trade networks connecting the two, they were likely aware of each other’s existence, but neither projected power onto each other.

184: Yellow Turban Rebellion (184-205); peasants suppressed by regional warlords; 3m-7m casualties

192: Civil Wars among regional warlords in Han China (192-220)

208: Warlord Cao Cao defeated at Battle of Red Cliffs by Sun Qian and Liu Bei; 100k casualties


220: Han dynasty ends (206BC-220AD), start Three Kingdoms period (220-265) with Wei in North, Wu in South East, Shu (Han) in South West.

263: Cao Wei conquers Shu Han.
266: Sima Yan deposes Cao emperor; Cao Wei becomes Jin.
280: Jin dynasty (266-420) unites China

291: War of the Eight Princes (291-306)
383: Battle of Fei River; Jin victory against former Qin
386: Jin dynasty breaks down into Start Northern Wei and Southern Qi dynasties (386-589)
581: Sui dynasty China (581-618), Grand Canal expanded, capital Xi’an, Confucianism disintegrated, making way for Taoism and Buddhism
590: Sui unites China under Yang Jian
598: Gorguyeo-Sui War (598-613) begins; 1m Sui troops invade Gorguyeo.
612: Gorguyeo defeats Sui invasion at Battle of Salsu; 300k casualties (2nd deadliest to date)
618: Tang dynasty China (618-907); Li Yuan first emperor


647: Gorguyeo repels Tang invasions (647-648 and again in 661 with 350k men)
666: Silla (allied with Tang) unifies Korea; Tang annexes most of Gorguyeo territory
690: Empress Wu (r. 690-704), only empress in Chinese history
751: Arab-Turkic-Tibetan alliance defeat Tang in Central Asia (Battle of Talas)
800: Chinese alchemists seeking elixir of life produce gunpowder instead
842: Tang dynasty persecutes non-Chinese religions (inc Buddhism and Christianity)
874: Warlords seize power as peasant rebellions undermine Tang authority (874-884)
906: Tang dynasty (618-906) collapses; start Five Dynasties period and Ten Kingdoms, China (907-960)
938: Vietnamese defeat Chinese at Battle of Bach Dang; ending 300 year Chinese rule
960: Song dynasty (960-1279) unifies China; Song Taizu first emperor; best living standards in world, gunpowder, printing, paper money, compass
1004: Song dynasty agrees to pay tributes to Khitan Liao
[work in progress]

[work in progress]
1556: Shaanxi earthquake; worst natural disaster in recorded history (1M died)

[work in progress]

1644: Qing army captures Beijing, marking end of Ming and start of Qing dynasty over China.
1645: Hairtyle massacre. Dorgon, the regent ruling on behalf of child emperor Shunzi enforces queue hairstyle. “Keep your hair, lose your head; keep your head, cut your hair.”
Begin 135 years of Qing Kang-Qian golden era of 3 emperors (1661-1796)
1661: Kangxi, longest ruling emperor in Chinese history begins reign (r. 1661-1722)
1722: Emperor Yongzheng (r. 1722-1735)
1736: Emperor Qianlong brings empire to it sheight (r. 1736-1796)
1793: Chinese demand for their tea, silk, and ceramics to be paid for in silver. Opium schemes from Western powers begins.
1839: Qing commissioner sent to Canton and burns 20,000 chests of opium and bans British trade.
1861: Empress Dowager Cixi takes control (1861-1906)
1912: Last emperor Puyi made to abdicate at 6 years old
1934-1935: Mao pulls off the Long March

1936: Xi’an Incident. Chiang Kai-shek detained by his generals to abandon KMT’s old policy of “first internal pacification, then external resistance” to aligning with the Communists against the Japanese.
1945:
China just before Japanese surrender.

Soviet Union invades Manchuria weeks before Japanese surrender, then hands it over to the Communists.

1949:
– (Oct 1) Mao defeats Nationalist army of Chiang-Kai-shek, ending civil war and founds People’s Republic of China
– (Dec) Kuomintang establish Republic of China in Taiwan


1950:
– (Feb) Mao and Stalin sign Treaty of Friendship, Alliance, and Mutual Assistance
– (Nov) China enters the Korea War and drive Allies back to 38th parallel. Fighting continues with more casualties and no major territorial gain on either side for next 2.5 years.
1953: Stalin, whom Mao respected, dies; Mao disapproves of new leader Kruschev
1954:
– China-Pakistan Military Aid Pact
– US-Taiwan Defence Treaty; First Taiwan Strait Crisis
1955: US passes Formosa Resolution; allowing US president to use force to defend Taiwan
1956: Hundred Flowers in Mao China; freedom of opinions
1958: Mao China launches “Great Leap Forward”, a 5-year plan to collectivize agriculture and industry; but abandoned after 2 years; economy contracts by 25%, 20m-40m die of starvation making it the largest famine in human history

1959: Tibet uprising suppressed

1960: Soviet Union shifts from being ally to enemy to China
1964: China becomes nuclear power
1965: Tibet War
1966: Cultural Revolution (1966-1976) in Mao China; a sociopolitical movement aimed at purging traditional elements and intellectuals.

1967: China explodes hydrogen bomb
1969: Sino-Soviet clashes at Xinjiang, but further escalations prevented by diplomacy
1971:
– (Jul) US secretary of state Kissinger secretly visits China
– (Oct) Mainland China joins UN while Taiwan is expelled.
1972: (Feb) Nixon visits China spooking Soviet Union and Vietnam

1974: Terracotta Army discovered (Qin army to guard emperor tomb)
1976:
– (Jan) Vice chairman Zhou Enlai dies
– (Sep 9th) Mao dies; “Gang of Four” including Mao’s widow vies for power but are arrested for crimes against the state.

1978: Deng Xiaoping (r. 1978-1991) emerges as China’s leader following Mao’s death in 1976; launches economic reforms (Open Door Policy), starting with agriculture.
1979:
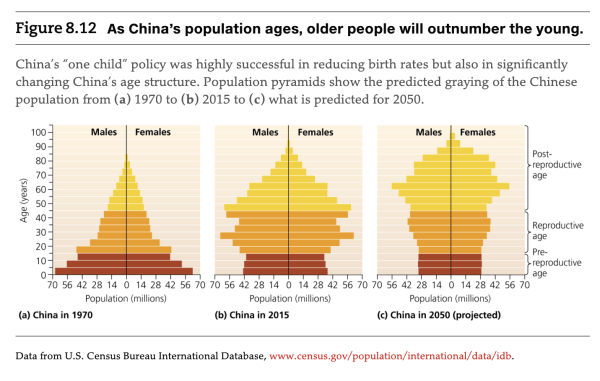
– One Child policy in China (1979-2015)
– (Jan) US officially recognizes People’s Republic of China
– (Feb) Deng Xiaoping China invades Vietnam briefly before withdrawing; to deter Vietnam expansionism
1989: (Jun 4th) Tienanmen square protests massacre; student-led democracy movement following death of Hu Yaobang (political leader that pushed for reforms)


1990: Pudong area within Shanghai becomes Special Economic Zone (SEZ) with even more flexibility than the original four SEZs earlier.

1992:
– Jiang Zemin takes over as Chinese Communist Party general secretary.
– Deng Xiaoping tours Southern China to quell influence of Party conservatives opposed to market liberalization
– Falun Gong founded
1995: China tests missiles and holds military exericses in Taiwan Strait.
1996: (Mar) Third Taiwan Strait Crisis: China conducts missile tests to discourage Taiwan from holding referendum; US sends 2 aircraft carriers
1997:
– (Feb) Deng Xiaoping dies; separatist terrorist attacks in Xinjiang on Deng’s funeral day
– (1st Jul) China regains sovereignty over HK from UK; One country two systems
1999:
– China regains Macau from Portugal
– (May) US Embassy in Beijing attacked by protesters after US (accidentally) bomb embassy in Belgrade during NATO bombing of Yugoslavia – symbolizes rising anti-US sentiment in China

2001: (Nov) China joins World Trade Organization, marking new phase in globalization

2002: Hu Jintao succeeds Jiang Zemin as head of Communist Party
2003:
– (Mar-Apr) China and HK hit hardest by SARS outbreak
– (Oct) China first manned space flight

2006:
– (Jul) Three Gorges Dam opens (construction began 1994)
– (Jul) China-Tibet railway opens

2007: (Feb) China president Hu Jin Tao tours 8 African countries for trade and investment.
2008:
– (May) Earthquake in Sichuan kills tens of thousands.
– (Aug) Beijing hosts Olympics, showcasing ‘new China’ to the world
– (Sep) Sanlu (state-run company) contaminated baby milk powder case (300k fall ill)
– (Nov) Chinese govt announces $586b GFC stimulus package.



2009: (Feb) $25b Russia-China deal; Russia supplies oil for next 20 years; China supplies loans.
2010:
– (Mar) Google leaves China after its services are blocked; YouTube blocked year before after Tibetan suppression footage uploaded, Facebook blocked after 2009 Urumqi riots
– (Oct) China VP Xi Jinping becomes vice-chairman of Central Military Commission
– (Dec) Activist writer Liu Xiaobo receives Nobel Peace Prize, but is unable to collect it (dies in prison in 2017 after 11 year sentence)
2011: (Jul) High speed rail derails in Wenzhou, highglihting aggressive peace of rail expansion


US Treasury holdings throughout the 2010s, and now it’s subsided to levels a decade ago.

2013:
– China launches Belt and Road Initiative.

– China starts building artificial islands in South China Sea

– (Mar) Xi Jinping becomes president of China; launches anti-corruption drive and consolidates his power.
– (Dec) China lands robotic rover on moon, first soft landing in 37 years
2014:
– (Sep) ‘Umbrella movement’ in Hong Kong, protesting for genuinely representative direct elections, shuts city down for 3 months but ends with no results
2015: (Nov) China’s Xi and Taiwan’s Ma hold historic talks in Singapore, first such meeting since 1949.
2017:
– (Jun) New cybersecurity law in China gives government even more control over company data, domestic and foreign.
– (Jul) China issues AI plan
– (Oct) Xi Jinping’s name and ideology amended into constitution, elevating him status on par with Mao’s.
2018:
– (Mar) Constitution amendment removes tenure limitations on Chinese presidency, allowing Xi to remain in power indefinitely.
– (Apr) China imposes 25% tariffs on range of US imports in response to similar measures by US.

2019:
– (Mar19-late20) HK extradition bill protests
– COVID-19 spreads globally from Wuhan
2020:
– China enforces strongest COVID-19 lockdowns in world for next 3 years


See also:


